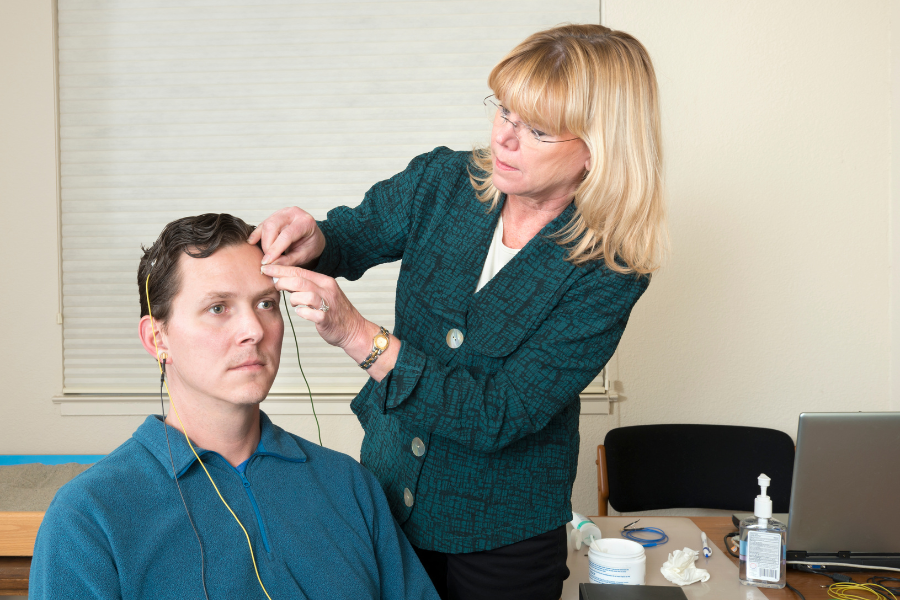
Biofeedback is a technique that uses visual or auditory feedback to help you learn how to control some of your involuntary bodily functions, such as blood pressure and heart rate. Biofeedback is used to help manage or treat various physical and mental health problems, which include:
- Anxiety
- Stress
- Asthma
- Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder
- Chronic pain
- Constipation
- High blood pressure
- Stroke
- Urinary or fecal incontinence
- TBI symptoms relating to headaches, attention, mood, and mindfulness
Biofeedback measures blood pressure, brain waves, heart and breathing rate, muscle tension, and skin temperature and conductivity of electricity. There are many types of biofeedback. These include:
| Type of Biofeedback | Description |
| Brain waves |
|
| Breathing |
|
| Heart rate |
|
| Muscle contraction |
|
| Sweat gland activity |
|
| Skin temperature |
|
References:
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/wellness-and-prevention/biofeedback
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5580369/
https://www.aapb.org/files/publications/biofeedback/2015/biof-43-01-31-37.pdf