Why Are Traumatic Brain Injuries and Concussion Symptoms Worse in the Summer Heat?
If you’ve experienced a head injury, you may already know that an array of symptoms can occur after the injury for days, months, and even years.
Brain trauma can cause body temperature regulation problems like feeling cold with chills, shivering, sweating, or hot flashes that come and go with no rhyme or reason. These elusive symptoms are very real, contrary to TBI myths like if you don’t have to have a loss of consciousness at the time of injury to experience severe neurological problems.
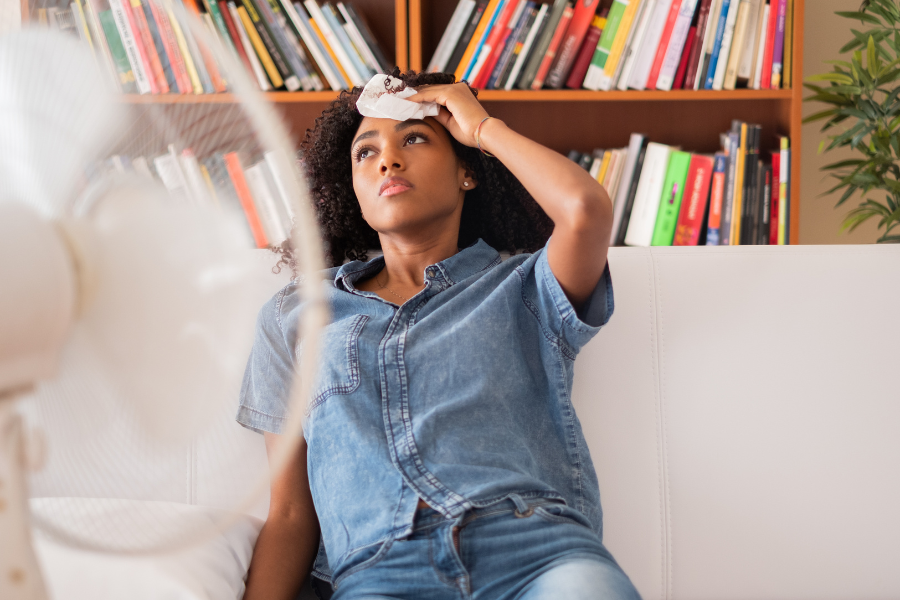
In oppressively humid weather a non-injured person can feel tired, nauseous, dizzy or light-headed, but a Traumatic Brain Injury survivor may experience more fatigue and headaches in the hot summer months.
Is it because of more daylight hours for light sensitive brain injuries?
Is it because it’s easier to get dehydrated which can make headaches and fatigue worse?
Is it because of increased activity outside in the heat like mowing the lawn or just walking across a hot parking lot?
All of these factors are true and contribute to the worse TBI symptoms in the summer months but there is scientific research to explain the phenomenon as well.

The Brain is Vulnerable to Heat
The brain is more vulnerable to heat because it can’t sweat like the rest of your body does to dissipate heat. The brain depends on blood flow from the rest of the body to cool down and this is a slow process. The brain stays at a higher temperature for a longer time than the rest of the body thus making it more vulnerable to high temperatures in the summer. A TBI makes it harder for the body to control temperature.
Normal body temperature can range between 97 F and 99 F or more and can vary depending on the time of day or activity levels. The brain controls temperature inside the pituitary gland and research is finding more TBI patients who have pituitary issues so brain injury can interfere with the body’s ability to cool down.
What is Thermoregulation?
Temperature in the body is strictly regulated by what is called the homeostatic process, which means the body does everything it can do to keep the same temperature when it’s hot or cold. Body temperature that is low can slow down the activities of cells and organs making processes like thinking and eating a challenge.
A body temperature that is too hot speeds up activity that can damage brain cells and organs. This process is controlled by the hypothalamus in the brain and by the autonomic nervous system that are in constant communication about body temperature. There are also secondary processes that influences body temperature that include diet, metabolism and hormones.
Why TBI Affects Thermoregulation
Brain injuries can interfere with the body’s temperature regulation because they affect all of the body’s systems and hormones.
TBI patients do not realize that even a mild concussion can result in system-wide health issues like:
- Disruption in neurovascular coupling
- Hypothalmus functions
- Hormone imbalance
- Elevated resting heart rate
- Perception of temperature
Patients who are struggling with lingering traumatic brain injury symptoms should seek support and a treatment plan designed to address their needs.
Head Injuries Can Cause Fever
Researchers say that up to 37% of TBI patients experience fever that is not caused by an infection but instead is completely neurological. This is called a neurogenic fever. Most of the time this is a short-term symptom but unfortunately it is linked to worse outcomes for the patient and in some extreme cases life threatening.
If a patient has had a concussion or head trauma and is experiencing a fever of over 100 degrees then they should seek medical treatment and a neurological evaluation, even if it wasn’t recent.
A traumatic brain injury patient can experience heat related symptoms for months after injury.
- Hot flashes
- Localized flushing and redness
- Body temperature elevations or chills
Medications and Supplements
Some supplements and medications prescribed for brain injury can affect how the body regulates temperature.
Some medications can increase side effects in hot weather, like making skin more sensitive or causing temperature regulation to fluctuate.
Always check possible side-effects on the bottle and online and speak to your doctor about the potential consequences of the medicine. Make sure that medications are stored at the recommended temperature and do not store in direct sunlight, like on a windowsill.

How to Cope with Post-TBI Body Temperature Regulation
People with impaired cooling mechanisms means their brains are no longer able to regulate core temperature. If a patient is experiencing body temperature issues post-TBI symptoms that’s a clear indication of brain function that is still affected by injury.
Receiving the correct diagnosis for treatment is key to getting the patient to start feeling better. The next steps may be for an endocrinologist to check out hormone regulation to help manage body temperature.
Body temperature regulation after a Brain Injury requires planning around it and having a checklist. It means drinking plenty of water, eating snacks, and checking the weather app.
In hot weather limit engaging in strenuous activity outside, exposure to hot weather, and excessive clothing. Stop all outside activity, Loosen clothing, rest in a cool place, and drink plenty of water.