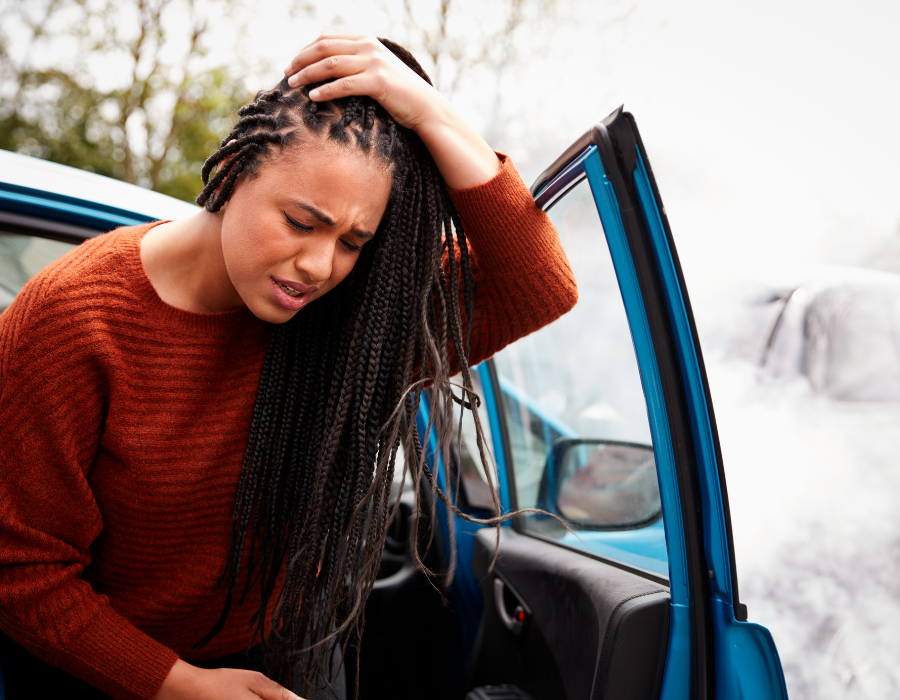
Brain injuries can happen to anyone, at any age and at any time. Whether it is from a car accident, fall or sports-related incident, knowledge of how brain injuries are categorized is key in understanding their severity and the potential for recovery.
According to the Center for Disease Control and Prevention, it is estimated that annually, about 1.5 million Americans survive a traumatic brain injury. Among these, approximately 230,000 are hospitalized.
A brain injury can be divided into one of two categories: traumatic and acquired.
Traumatic brain injuries occur when there is a forceful bump, blow, or jolt to the head or body, or from an object that pierces the skull and enters the brain. Not all blows or jolts to the head result in a TBI. They can happen in one of two ways: closed injury or penetrating injury.
A closed brain injury (non-penetrating) occurs when there is no break in the skull, also known as a non-penetrating brain injury. This can be a rapid forward or backward movement and shaking of the brain inside the bony skull that results in bruising and tearing of the brain tissue and blood vessels. These types of traumatic brain injuries can be caused by a car accident, fall, a hit from playing sports, a blast injury, an assault and even shaking a baby, which is known as shaken baby syndrome.
A penetrating injury, also known as an open head injury, occurs when there is a break in the skull. This can occur when a bullet pierces the brain, by shrapnel, bone fragment, or by a weapon such as hammer or knife.
A diffuse axonal injury is another type of traumatic brain injury. These types of injuries occur when there is shearing of the brains long connecting nerve fibers. This happens when the brain is injured as it shifts and rotates inside the skull. These injuries usually cause a coma and injury to different parts of the brain. These are often microscopic and may not be seen on a CT or MRI scan.
A coup-contrecoup brain injury is another type of traumatic brain injury. This type of injury occurs when there is significant impact to the brain that causes the brain or skull to slam into the opposite side of the site of impact. The result is damage at the impact site, as well as on the opposite side of the brain. Serious car accidents, blows to the head, forceful falls, and acts of violence typically produce these injuries.
An acquired brain injury occurs when there is an injury to the brain that is not hereditary, congenital, degenerative or induced by birth trauma.
An acquired brain injury can happen with a stroke, a brain tumor, a brain infection or inflammation or an anoxic or hypoxic injury.
Hypoxic brain injuries occur because of a restriction of oxygen supply to the brain. The restricted oxygen flow to vital parts of the brain will cause the gradual impairment and death of brain cells. Anoxic brain injuries result from the brain being deprived of oxygen for prolonged periods.
Brain injuries can also be primary and secondary.
A primary brain injury is the sudden and profound injury to the brain that is more complete or less complete at the time of the impact. This would happen at the time of a car accident, fall, or even a gunshot wound.
A secondary brain injury is changes that evolve over a period of hours and even days after the primary brain injury. This includes an entire series of stages of cellular, chemical, tissue or blood vessel changes in the brain that contribute to further destruction of brain tissue. Secondary brain injuries are often the leading cause of brain damage or death that began with a primary brain injury.
Brain injuries can have a lasting impact on one’s life. They can range from a mild injury like a concussion, to a devastating injury such as a stroke or a traumatic brain injury. Since injuries range it is difficult to predict how someone may be affected by their injury, and what their recovery may look like.
Treatments for traumatic brain injuries are available and they can make all the difference in improving their quality of life. Neuropraxis offers up many resources to help one recover from a brain injury.
Neuropraxis offers physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, recreational therapy and life skills navigation. Additionally, Neuropraxis programs offer allow for home and community rehabilitation, in-home day treatment, transitional apartment living and in-home supported living.
Neuropraxis aims to provide a comprehensive and customized treatment program through evidence-based practices facilitating the transition of individuals with brain injuries to a life of purpose, social connection and optimism.
For more information, contact Neuropraxis at (888) 266-8921 or hello@neuropraxisrehab.com, or visit www.neuropraxisrehab.com.
To learn more about the recovery process, visit https://neuropraxisrehab.com/traumatic-brain-injuries-and-recovery/.
Resources:
https://www.healthline.com/health/brain-damage
https://www.ninds.nih.gov/health-information/disorders/traumatic-brain-injury-tbi
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/traumatic-brain-injury
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459300/
https://www.spinalcord.com/types-of-traumatic-brain-injury
https://www.biausa.org/brain-injury/about-brain-injury/basics/overview