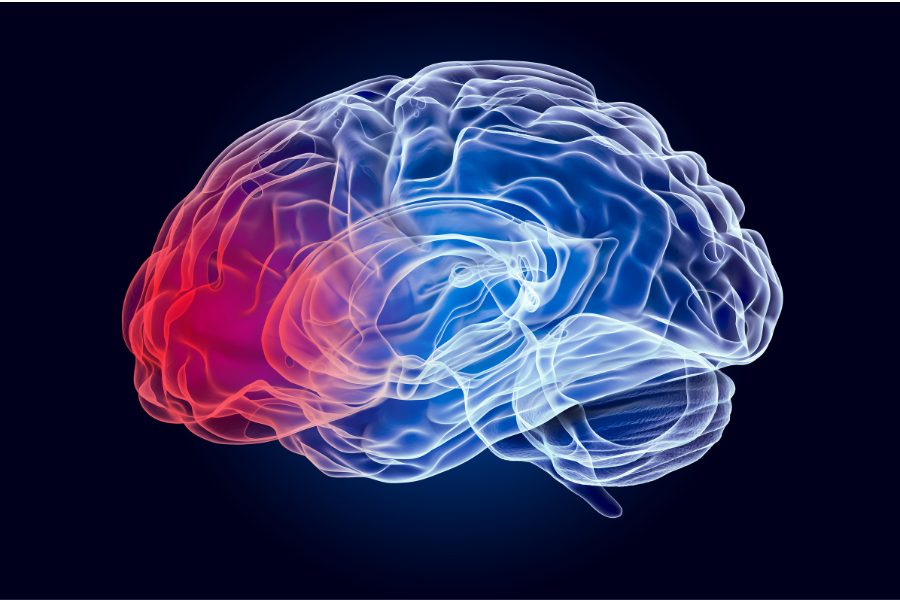
The brain consists of four lobes on the left and right side: the frontal lobe, the parietal lobe, the temporal lobe, and the occipital lobe. Each lobe has different functions.
The frontal lobe controls our executive function, which is a set of complex mental skills needed to help us learn new information, retain information, and use information to solve everyday problems. Here are some common executive functions that we may use in our everyday lives:
| Executive Function | Definition | Example |
| Planning | The process of thinking ahead to complete a task or goal | Writing down when your school assignments are due on a planner |
| Organizing | Grouping something in order or into a structured whole | Alphabetizing folders by last name at your job |
| Initiating | To start or begin a process or action | Asking someone of his or name to start a conversation |
| Sequencing | Doing or arranging something in a particular order | Following a recipe to cook a meal |
| Problem-solving | Finding solutions to problems | Asking your professor for help on homework |
| Attention | The ability to focus on someone or something for a certain amount of time and shifting that focus when needed | Being able to read your book with the TV on |
| Working Memory | The ability to keep information in your mind while using it | Dialing a phone number you just learned onto your phone |
| Emotional Regulation | The ability to control your emotions in challenging situations | Controlling your anger while driving during traffic hours |
| Impulse Control | The ability to stop and think before doing something | Choosing not to speed while driving to prevent a car accident |
| Flexibility | The ability to adapt to unexpected changes by changing strategies or behavior | Taking an alternative route to work due to unexpected road closures |
| Self-Monitoring | The ability to monitor and evaluate yourself | Being aware of your table manners when eating at a restaurant |
These cognitive skills are important because they help us perform our everyday activities and routines more easily, functionally, and safely.
Additionally, the frontal lobe has many other functions that play a role in our daily lives. These include:
| Function | Description |
| Speech and Language Production | Broca’s area, which is part of the frontal lobe, helps put your thoughts into words. |
| Controlling Voluntary Movement | The primary motor cortex, which is also part of the frontal lobe, helps you move your body consciously, such as for running or walking. |
| Comparing Objects | The frontal lobe helps you categorize and classify objects and distinguish one object from another. |
| Understanding the Feelings of Others | The frontal lobe is associated with our ability to feel empathy. |
| Personality Development | The frontal lobe is home to our personality, |
| Motivation and Reward-seeking Behavior | The frontal lobe has many dopamine neurons. Dopamine is a chemical that supports our feelings of motivation, reward, pleasure, and happiness. |
Damage to the frontal lobe may cause a variety of symptoms. Some of these symptoms may include:
- Loss of movement, either partial (paresis) or complete (paralysis), on the opposite side of the body
- Difficulty performing tasks that require a sequence of movements
- Trouble with speech or language (aphasia)
- Poor planning or organization
- Persistence with one behavior, way of thinking, or set of rules
- Difficulty with higher order functions, such as reasoning, problem-solving, and judgment
- Difficulty maintaining attention or concentration
- Decrease in motivation
- Mood swings
- Impaired ability to initiate activities or interactions
- Drastic changes in personality or behavior, which can include apathy, irritability, and inappropriate social behavior
- Poor impulse control or lack of inhibition
However, there are general strategies to use for individuals with a frontal lobe injury. Some of these strategies are:
- Using a planner or calendar
- Using effective electronic apps, i.e., reminder calls/alarms
- Playing memory and/or brain games
- Determining triggers of behavior
- Yoga or Meditation
- Journaling
References:
https://www.health.qld.gov.au/abios/asp/bfrontal
https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/318139#Functions-of-the-frontal-lobe