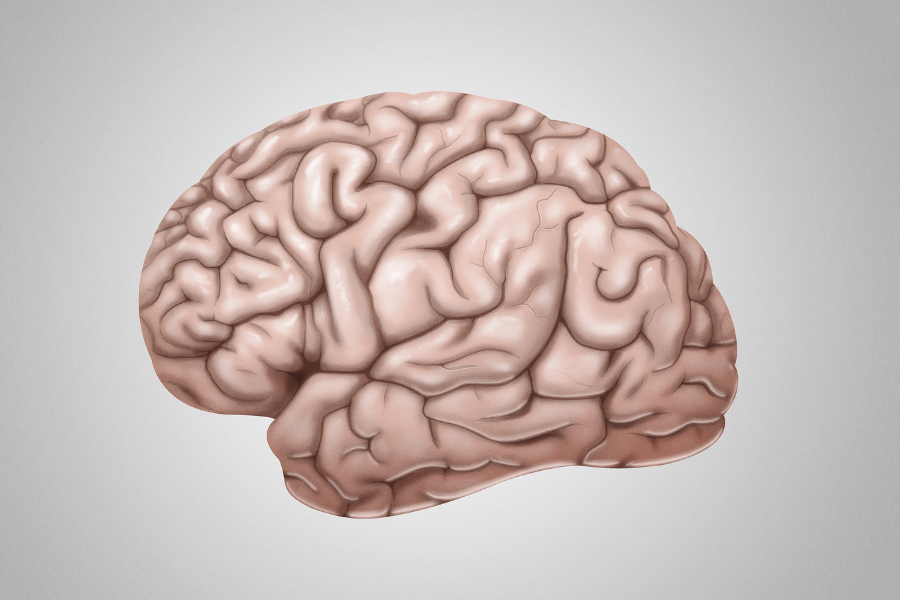
The cerebrum is the part of your brain that controls muscle functions. It is divided into two hemispheres: a left hemisphere and a right hemisphere. Each hemisphere receives sensory information from the opposite side of the body. The left hemisphere controls your right side of the body, and your right hemisphere controls your left side of the body. The two hemispheres are also responsible for different functions.
| Left Hemisphere: The “Rational” Side | Right Hemisphere: The “Intuitive” Side |
|
|
Damage to the hemispheres may lead to different outcomes, depending on which hemisphere is affected.
| Damage to Left Hemisphere | Damage to Right Hemisphere |
|
|
There are general strategies that affected individuals can use to treat these symptoms.
- Try seeking speech therapy, occupational therapy, and/or physical therapy
- Avoid neglecting the affected side of your body.
- Try using the affected arm as much as possible (if you can), even with the help of your non-affected arm.
- Put objects on the neglected side so you can attend more to that side more often
- Practice visual scanning techniques to help with impaired visual field. Examples include:
- Putting brightly colored tape on left side of book to help you look at the left side first, then you can practice reading from left to right
- Playing iSpy or Spot the Difference
- Breaking down a task into smaller components if the task is too difficult
- Reduce distractions to help with attention (i.e., turn off TV)
- Engage in mobile apps, games, or brain exercises that aim to improve cognitive skills, such as memory, attention, and problem-solving (i.e., Lumosity)
References:
Kalat, J. W. (2017). Biological Psychology. Cengage.
https://my-ms.org/anatomy_brain_part1.htm
https://bouve.northeastern.edu/nutraumaticbraininjury/braintbi-anatomy/brain-functions/
https://www.asha.org/practice-portal/clinical-topics/right-hemisphere-damage/#collapse_2